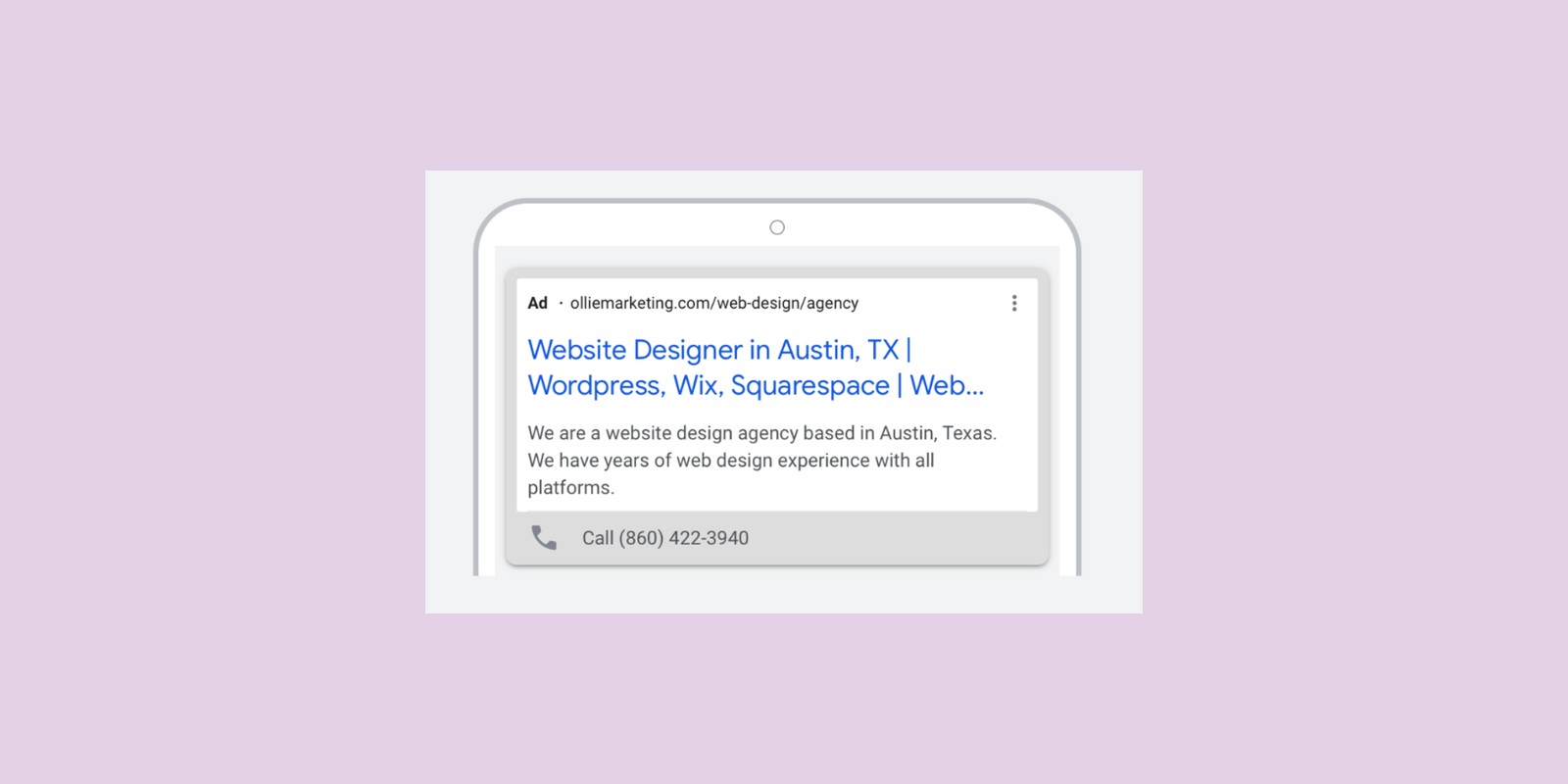
Since the platform was first launched in 2000, Google Ads has evolved into the world’s largest online advertising platform. Services are offered under the pay-per-click (PPC) model, although the option to pay per conversion is available within select campaigns and circumstances.
Within Google Ads, the user has access to a variety of campaigns including Video, Display, Gmail, and Search. This article will provide an overview of Google Search and offer a step-by-step guide on creating your very first Google search campaign.
Author Qualifications
I first gained exposure to Google Ads in 2018, shortly after I graduated from college. Since then, I have had the opportunity to build and manage Google search ads for over 50 brands.
My experience qualifies me to share with you how to set up an effective campaign, what has worked for me, and what hasn’t worked for me.
Benefits of Google Search Ads
Google search ads are a fantastic paid channel to add to your digital mix for warm traffic that is actively searching for your offer.
With a billboard, an advertiser can choose a location to place the ad. The majority of eyes seeing the ad may not be the advertiser’s target market.
With a social media advertisement, an advertiser can select interests, locations, and other filters to narrow down the audience.
With Google Search, the advertiser targets by keyword. This means you can catch people as they are actively researching your product or service.
The benefits of these campaigns are not limited. Google Search ads can:
- Reach potential customers who are actively searching for products and services related to your business.
- Target customers based on location, language, device type, and more.
- Get detailed insights into how people interact with your ad so you can make data-driven decisions.
- Control costs by setting a budget that works for you.
- Measure the success of your campaigns with custom reporting tools.
Google Search Campaign Structure
Before you can begin mastering Google search ad creation, it’s important to understand the structure of a Google search campaign. For all my visual learners, here is a chart highlighting the details.
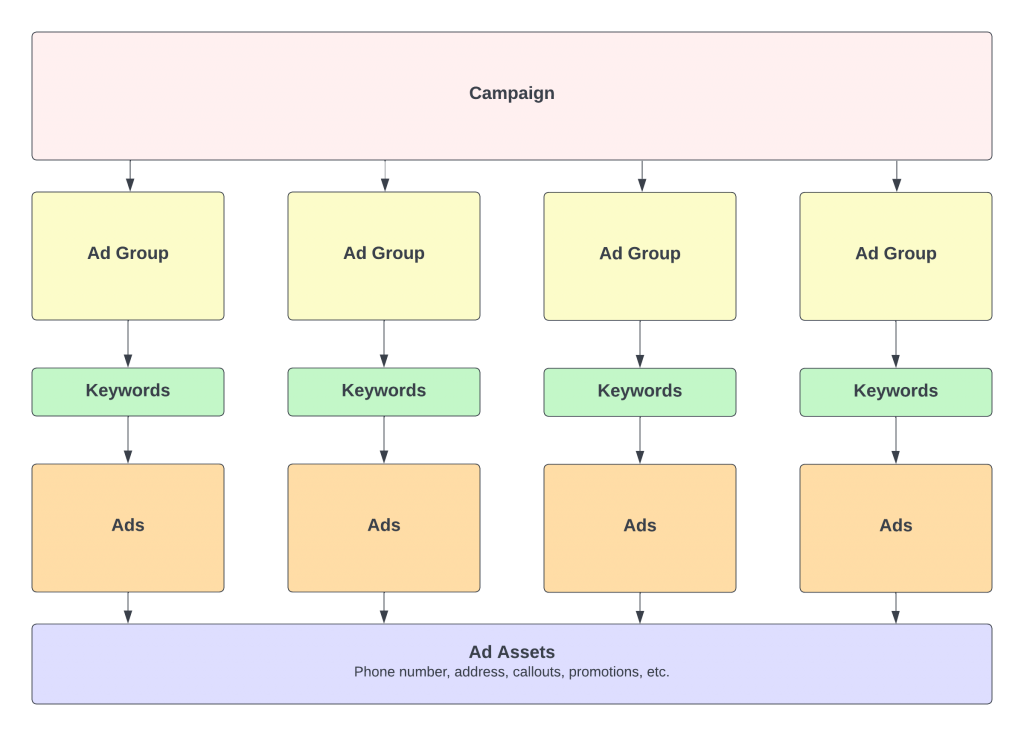
The campaign will contain your details like location and daily budget. These details will apply to any any groups and ads built within the campaign. For businesses with multiple locations, it may be advantageous to segment campaigns by each location.
The ad group will segment your landing pages and keywords. Each ad group will have their own ads. An electrician who offers commercial & residential electrical services may create separate ad groups for each service.
The ads will correspond with their ad groups. An ad group for commercial electrician services may point to the page on the website about this particular service (https://example.com/commercial-electrician-seattle). The ad headlines and descriptions will revolve around this particular service.
Ad assets are additional pieces of information that can be added to a search ad. In my experience, more assets = higher performance.
Some of these assets include:
Image extension – These are relevant visuals to complement your ads.
Call extension – A clickable phone number that lets the user call without leaving the search results.
Sitelink extension – Additional links from your website.
Callout extension – Additional touchpoint in regards to why the user should select your business.
Location extension – This extension integrates with your Google Business profile.
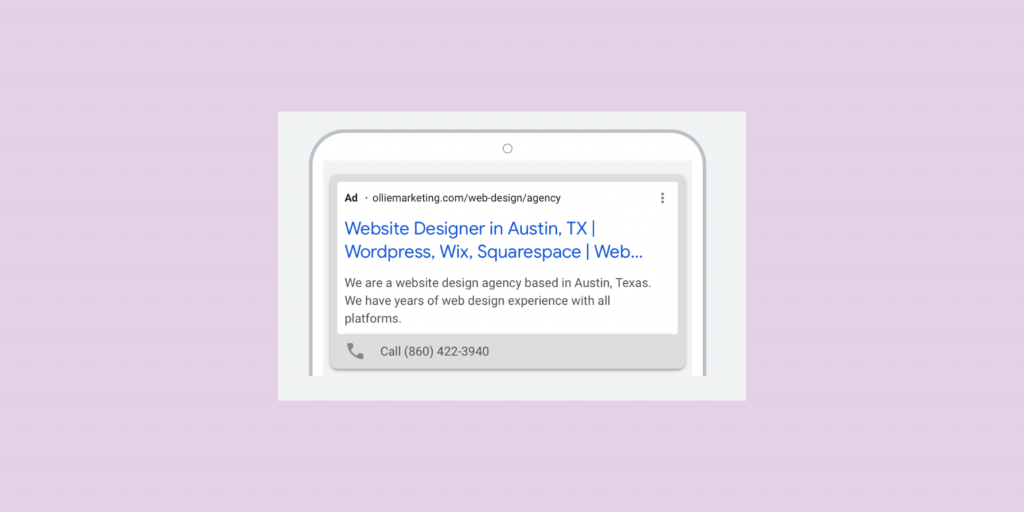
See below for an example of this structure in action. In this case, I build a test campaign for my marketing agency, focusing on web design & SEO as service offerings.
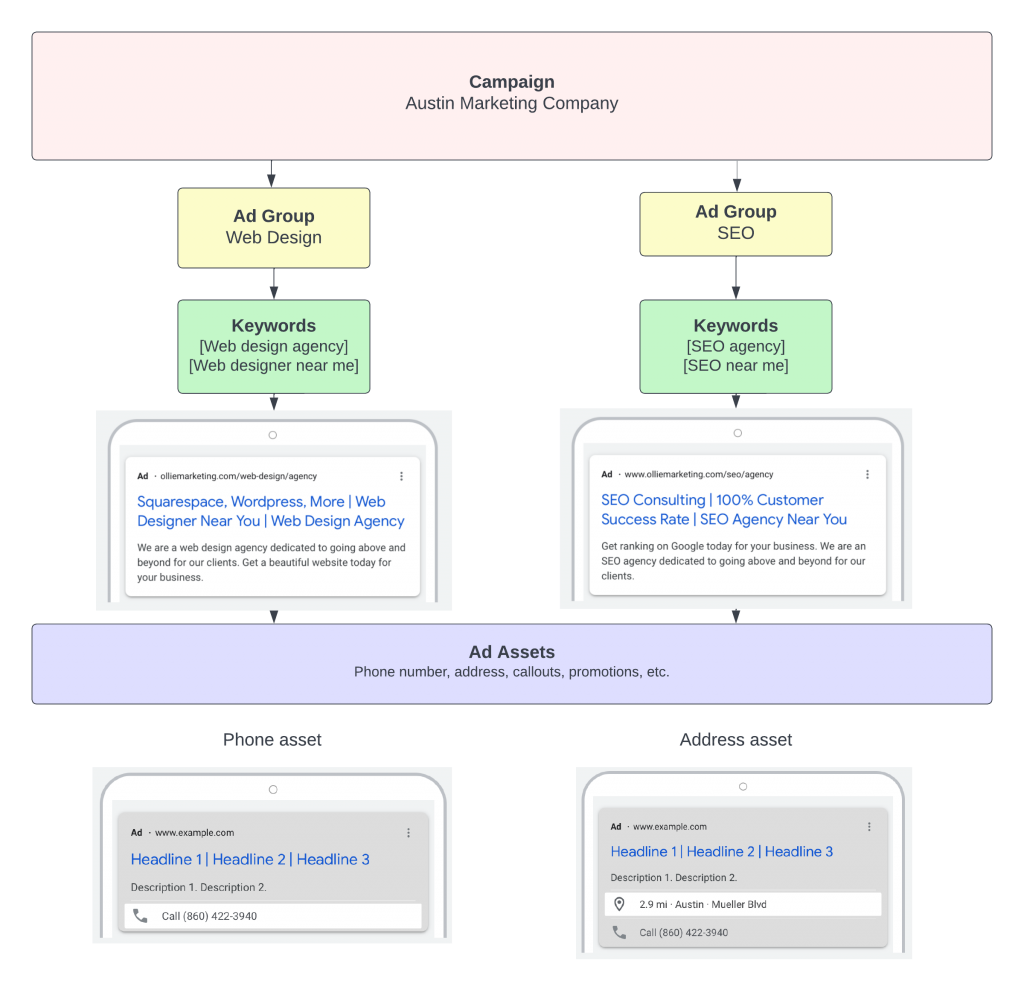
Building a Search Campaign Step-By-Step
We will now take you through the process of building your Google search campaign. For this walkthrough, we will build the campaign for my marketing agency based in Austin, Texas. The campaign will focus particularly on web design traffic.
Step 1. Access Your Dashboard
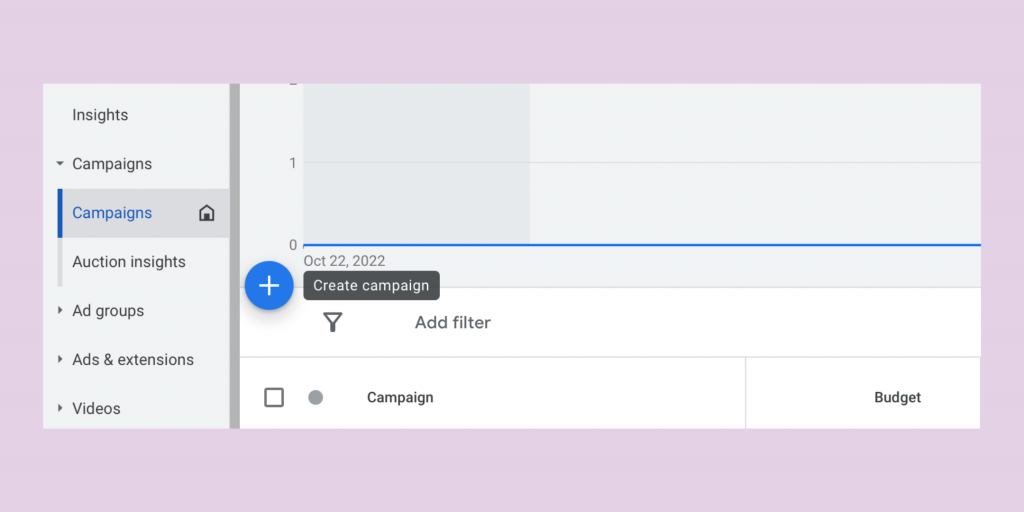
Using a computer, log in to https://ads.google.com to access your account. Once logged in, click on Campaigns on the left menu. Once you navigate to the Campaigns page, click Create campaign.
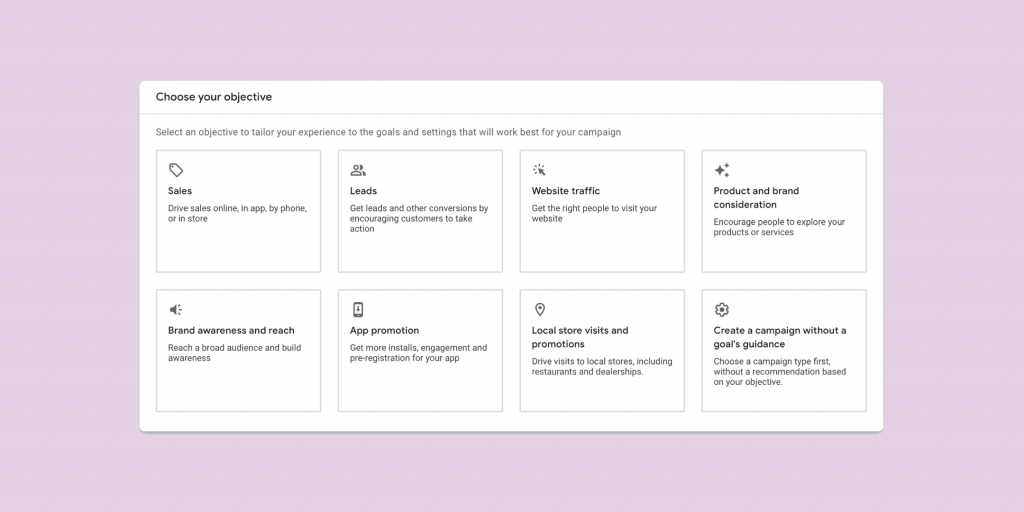
Step 2. Campaign Objective
On this page, Google provides a variety of goals to choose from including sales, leads, and website traffic. By selecting a specific goal, Google can modify future settings to simplify the campaign creation process.
On the bottom right, you will see an option that says Create a campaign without a goal’s guidance. Click this option. By opting to create a campaign without a goal’s guidance, we are provided access to all settings possible on later steps.
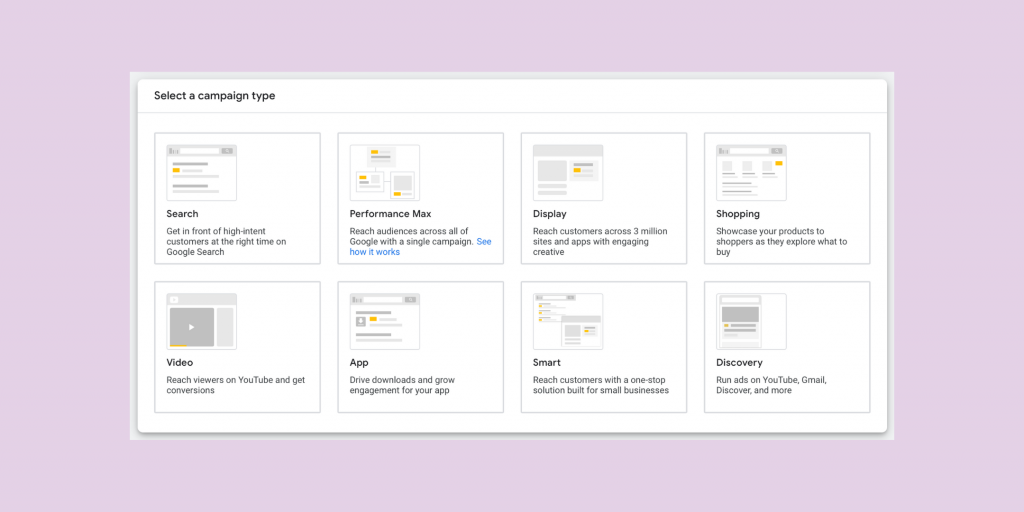
Step 3. Campaign Type
In this step, we narrow down the type of campaign to focus on. Some options include display, video, shopping, and search. We are going to select Search.
Step 4: Conversion Goals
Google will then request conversion goals to be added. If you don’t have conversion goals set up, you can choose to:
- Ignore this step.
- Watch this video to learn how to set up conversion goals.
To proceed to the next step, click Continue
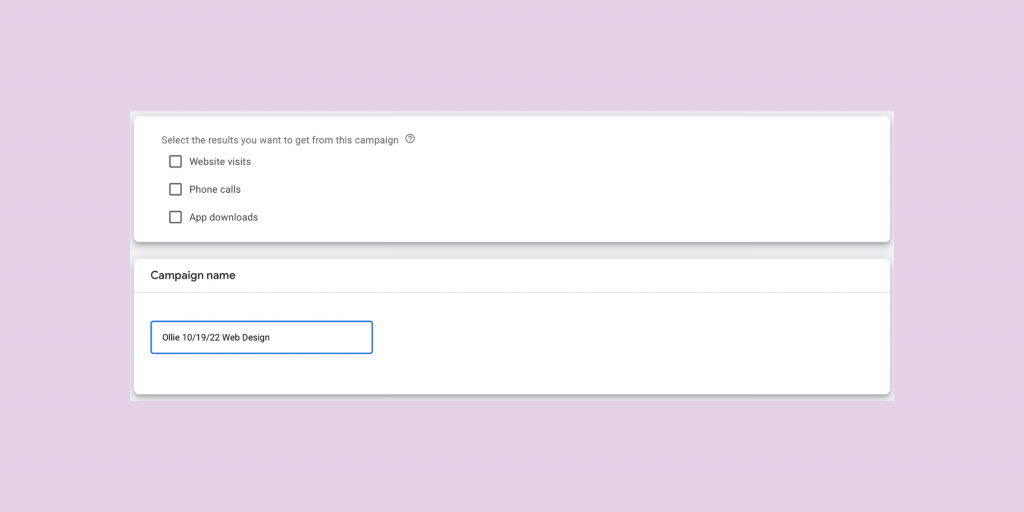
Step 5: Results / Campaign Name
You will now see two additional sections. The first will ask you what type of results you are looking for within the campaign. I leave this section empty. These details can be added later.
For the campaign name, we will add a name that helps differentiate from additional campaigns in the future. One example would be [brand name] + [date created] + [focus] (Ollie 10/19/22 Web Design).
Step 6. Bidding
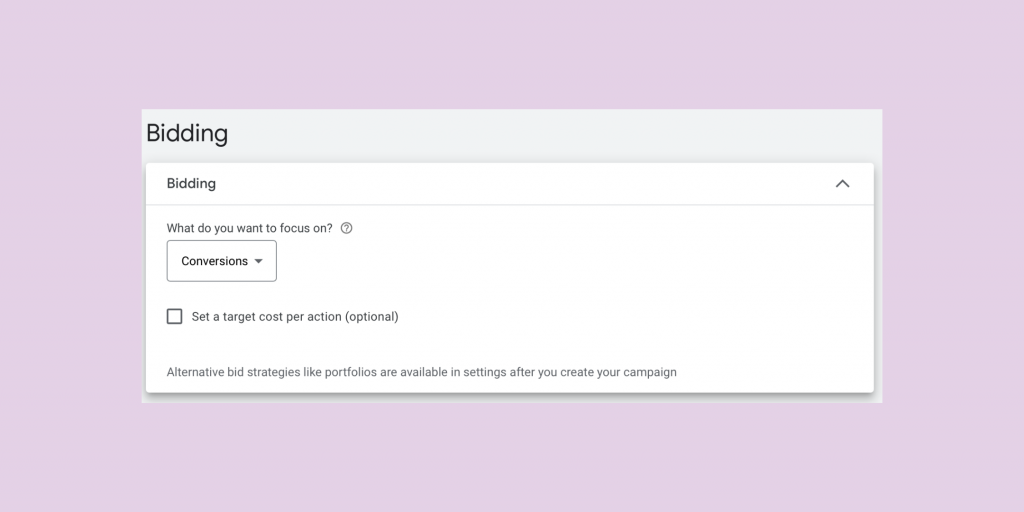
This step contains more nuances than previous options. On this page, we are going to select a bidding strategy for the campaign.
When a user searches for a keyword on Google that people bid for, an auction occurs in the milliseconds between when the user presses enter and reaches the results page.
Google uses three primary factors to determine which placements should show:
Bidding – The amount the advertiser is willing to pay to show an ad.
Quality Score – The relevancy of the landing page and ad copy.
Extensions (assets) – The number of extensions that are included within an ad.
How Much Should I Bid on Google Ads?
To determine how much you should be bidding for your target keywords, I recommend using the free Keyword Planner tool located inside of your Google Ads account. You can get to this tool from Tools & Settings -> Planning -> Keyword Planner.
With this tool, you can enter the keywords you are planning on targeting, enter the location you want to target, and Google will provide average bids on the low range and high range.
Which Bid Strategy Should I Choose?
To determine which bid strategy you should choose, consider the following. Do you have conversion tracking set up?
For accounts with conversion tracking in place, with the primary campaign goal being to get as many conversions as possible, a Maximize Conversions strategy can work well.
For a focus on where your ads are showing (Absolute top of page, anywhere on results page, etc.), a Target Impression Share strategy will work best.
For campaigns hoping to drive as much website traffic as possible within budget, Maximize Clicks will work best.
To learn more about each bidding strategy, read this article.
Step 7. Networks
Google offers two additional networks outside of traditional Search to include in your campaign.
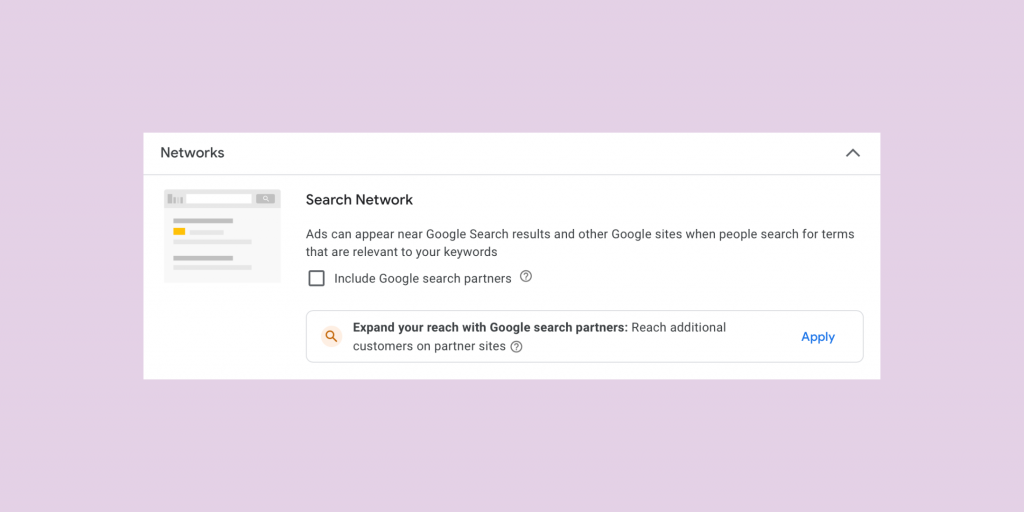
On the Search network, “Ads can appear near Google Search results and other Google sites when people search for terms that are relevant to your keywords”
On the Display network, “Easy way to get additional conversions at similar or lower costs than Search with unused Search budget.”
When I was first taught how to build Google Search campaigns, my instructor advised me to deselect these because the traffic is not as valuable and will waste ad spend.
After a few years of campaign audits, I have seen mixed results from campaigns that opt-in for these networks.
When I build a new campaign, I still choose to deselect these networks to focus primarily on Google Search placements.
Step 8. Locations
On the Locations section, campaigns can target by country, state, city, zip code, and even coordinates.
A local business may choose to target a radius around their business location, or ZIP codes within their service area.
A national brand may choose to focus on the whole United States. Choose a location that best fits your goals.
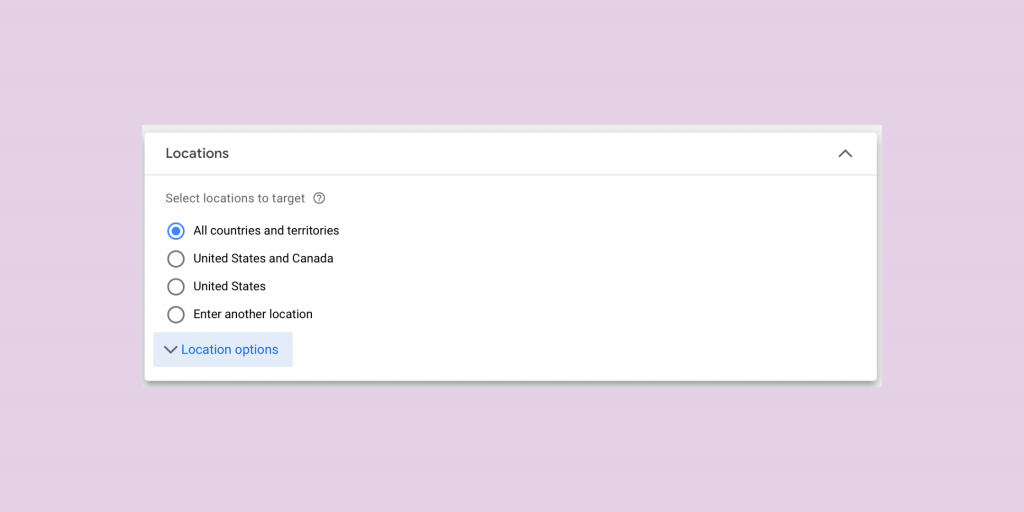
You will see a Location Options dropdown menu. Be sure to review the options offered. You can choose to target people searching for your locations or in your locations. If your customer needs to be close in proximity to you, be sure to select Presence.
There are scenarios where the other options are beneficial. Picture a landlord based in Minnesota searching for a cleaning company for a rental property in Vancouver. In this case, the cleaning company would benefit from choosing Search Interest as the location option.
Step 9. Languages
This is fairly self-explanatory. Determine which language your target customer speaks and what language your website is written in, and add those languages.
Step 10. Audience Segments
Audience segments can be added to narrow down your targeting range OR to observe and collect details for bid adjustments.
Some popular audience segments include:
Detailed Demographics – Parental status, education, homeowner status, etc.
Affinity – Food & dining, home & garden, sports & fitness, etc.
Personal Data Segments – Website visitors, YouTube visitors, etc.
Audience segments are not required for a successful search campaign.
Step 11. More Settings
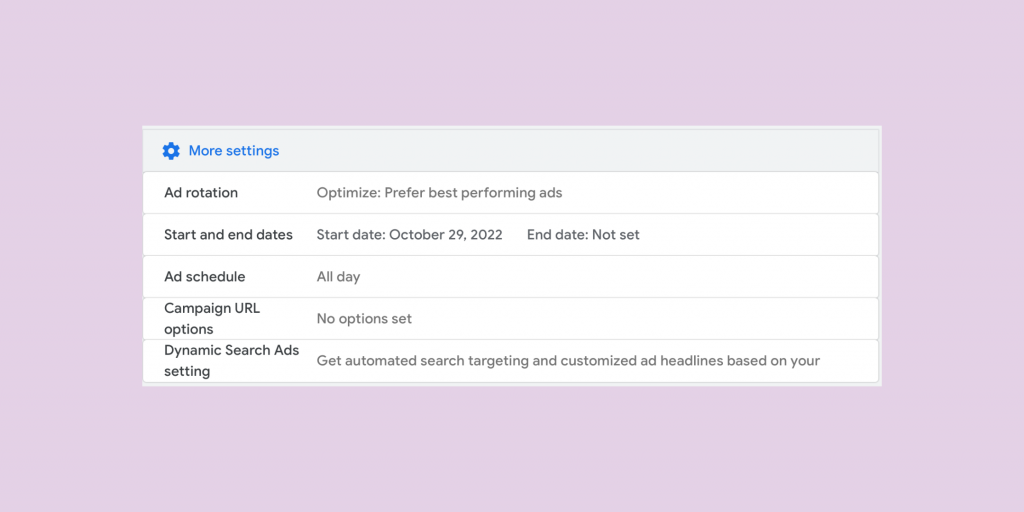
This dropdown section will offer the following additional settings to choose from:
Ad Rotation
Select between rotating your ads indefinitely or having Google optimize for which ads are likely to perform best.
Start & End Dates
If you would like to build a campaign with an end-date, this will be the area to enter the end point. If you don’t enter this date, the campaign will run until it is manually paused.
Ad Schedule
Choose what times and days ads should show. A business that is open 9am-5pm Monday-Friday may choose to only run ads during this schedule. Use this setting to make sure ads are running when customer support / phone calls are reachable.
Campaign URL Options
This setting is optional to set up custom URL parameters for measurement on platforms like Google Analytics. Here is a resource for more details on this setting.
Dynamic Search Ads
If you would like to have Google crawl your website to create automatic ads, enter the details in this area.
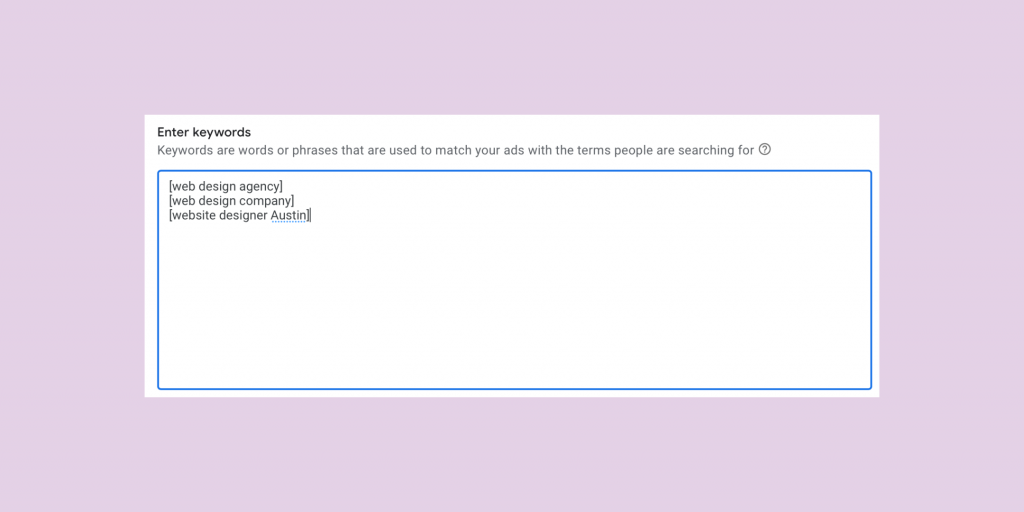
Step 12. Keywords
The Keywords section requires keywords to be added to the first ad group. An ad group should be named according to the campaign set up. In this campaign, we are only focusing on web design. We name the ad group Web Design.
In this section, it’s important to understand there are 3 different types of Google Ads keyword match types:
- Broad – searches that relate to your keyword
- Phrase – searches that include the meaning of your keyword
- Exact – searches that are the same meaning of your keyword
A campaign with all broad match keywords can expect the most impressions and less relevant traffic.
A campaign with all phrase match keywords can expect less impressions and more relevant traffic.
A campaign with all exact match keywords can expect the least impressions and most relevant traffic.
For the purpose of this example campaign, I opt for a campaign with 1 ad group that contains 3 exact match term keywords.
As keywords are added, Google will offer a forecast of estimated cost per acquisition, conversions, and clicks.
Step 13. Ads
Start by adding the final URL where traffic should go when clicking the ad. A page dedicated to the specific service can improve an ad ranking. In this example, I send them to my service page about web design.
Phone Assets
If phone calls are a goal for your campaign, select + calls to add a phone number to include in the ad.
Additional Assets
There are many additional assets that can be added to your ads. Be sure to include all that are relevant for increased campaign performance.
Headlines & Descriptions
Add up to 15 headlines. Be sure to include keywords similar to the keywords you are targeting. Headlines can be up to 30 characters each.
Add up to 40 descriptions. Describe why the customer should choose your brand. Descriptions can be up to 90 characters each.
Once you add all of these details, select Next on the bottom of the page.
Step 14. Budget & Review
For your daily budget, Google will offer some options based on the data entered in previous steps. You can select one of these recommendations or select set custom budget to choose your own budget.
Once complete, select Next on the bottom of the page.
Finally, review all of the details entered in previous steps. Once you are ready, select Publish Campaign.
And that’s a wrap! You have just built your own custom Google search campaign. Google will review your campaign and approve within 1-3 days. If there are any issues with the campaign, you should receive a notification through email.
-

Experienced tech journalist and freelancer with over 10 years of experience. Developed expertise in covering tools, new technologies and industry trends.